My ongoing research is situated at the intersection of AI and multimodal communication, focusing on two main areas: Human-AI Intelligence and Multimodal Representational Learning. Theoretically, my dissertation, titled "From Language Models to Multimodal Intelligence," explores these models within the framework of symbolic versus embodied cognition, leveraging various deep neural network (DNN) simulations and human-AI interaction studies.
In layman's terms:
Human-AI Interaction: This research primarily involves human-LLM interaction and human-language vision model interaction design to examine how human preferences align or deviate from those of generative AI models (e.g., image caption alignment). It also explores how our communication with large generative models is affected when pairing users with language-only and language-vision conditions. I work closely with my committee members to format my study design, including contributions from Dr. Elisa Kreiss's Computation and Language for Society lab and Dr. Hongjing Lu's Computational Vision and Learning Lab.
Additionally, I collaborate with complex systems scholars to use multi-agent LLMs to simulate how agent personalities impact problem-solving in negotiation games, and with social neuroscientists to examine individual differences in the biosignals associated with "feeling connected" in human-GPT-4o interactions.
Multimodal Representational Learning: This research can be broadly understood as Applied Deep Learning/Machine Learning with a Computational Cognitive Science focus. I utilize various combinations of deep learning models (CNN, RNN-LSTM, Transformer, Seq2Seq, etc.) for diverse goals, from improving classification performance for multimodal datasets, to facilitating downstream statistical analysis on de-spatialized/de-temporalized embeddings from raw signal forms, and conducting large-scale simulations on signal patterns of embeddings across models, modalities, and datasets. I work closely with my primary advisor, Dr. Rick Dale, and seek guidance from Dr. Hongjing Lu.
At Dr. Dale's Communicative-Mind (Co-Mind) Lab, I actively collaborate with social neuroscientists as DNN modelers to streamline the integration of neurosignals (fNIRS) with other behavioral signals (facial expressions, body movements), bridging the analysis of these raw signals with high-level social constructs (shared reality, connectedness, etc.).
Human-AI Intelligence
Multimodal Intelligence | Embodied Cognition | Human-Computer Interaction
Human-AI Intelligence + Cognitive Science
-
Jiang, Y., Dale, R., & Lu, H. (2023). Transformability, Generalizability, but Limited Diffusibility: Comparing Global vs. Task-Specific Language Representations in Deep Neural Networks. Cognitive Systems Research, 101184. doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsys.2023.101184.
-
Jiang, Y., & Dale, R. Mapping the Learning Curves of Deep Learning Networks. PLOS Computational Biology. (under review). https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2024.07.01.601491v1
Representational Learning + Computational Neuroscience
-
Jiang, Y. (2024). Unlocking the Complexity of Deep Learning in Neuroimaging: Insights into Within- and Cross-Modality Representational Similarities of fMRI-Autoencoders. Brain Research Bulletin. (under review)
-
Miao, G. Q., Jiang, Y., Binnquist, A., Pluta, A., Steen, F., Dale, R., & Lieberman, M. (2024). A Deep Neural Network Approach for Integrating Neural and Behavioral Signals: Multimodal Investigation with fNIRS Hyperscanning and Facial Expressions. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society (Vol. 46). https://escholarship.org/uc/item/2pj0b5qb






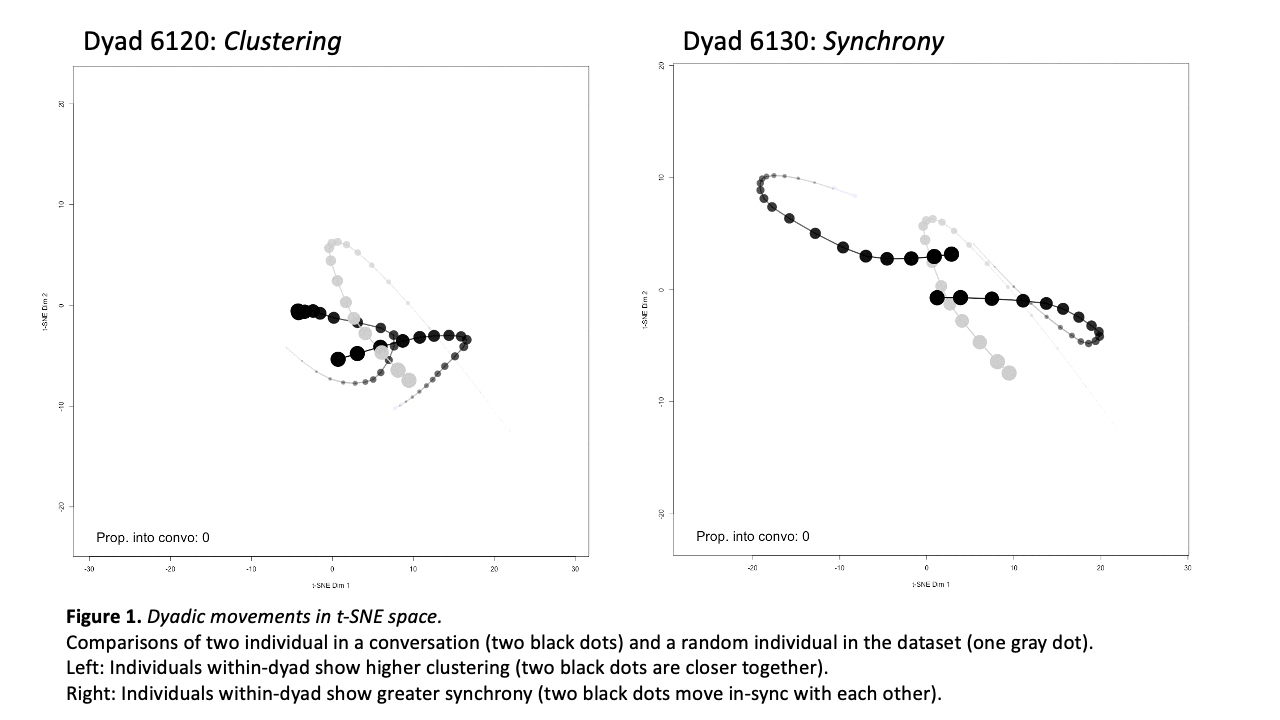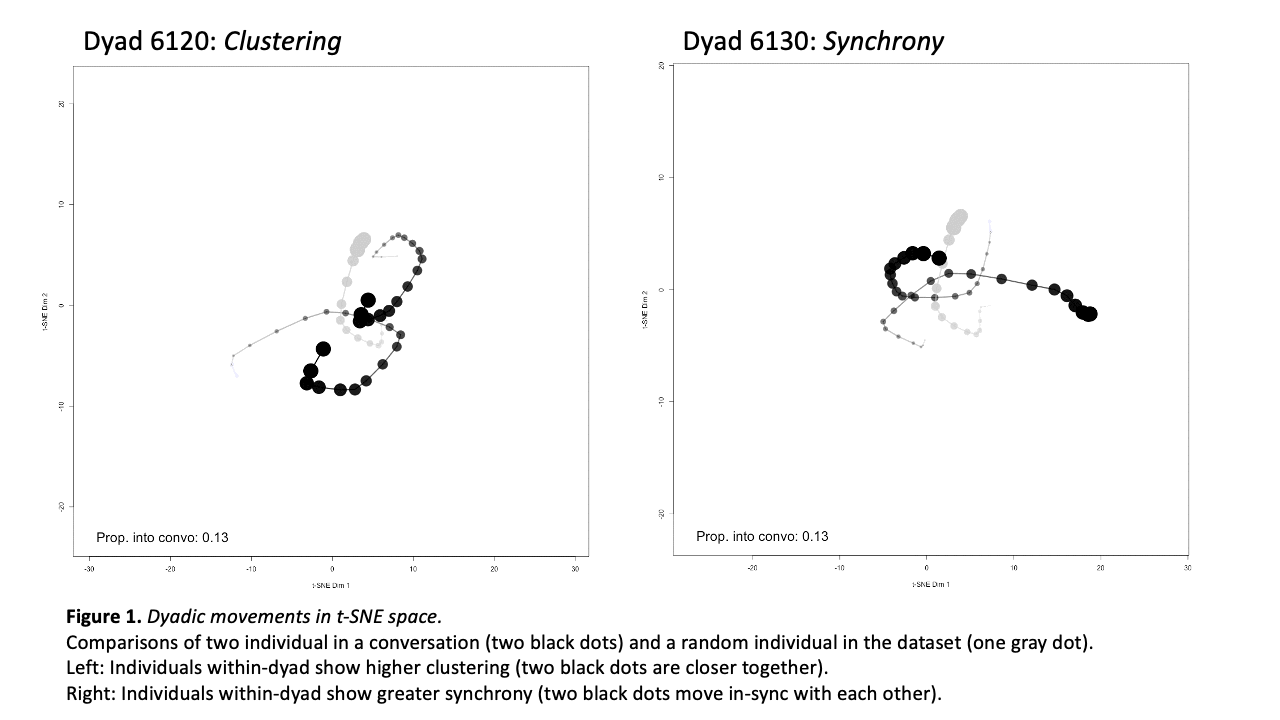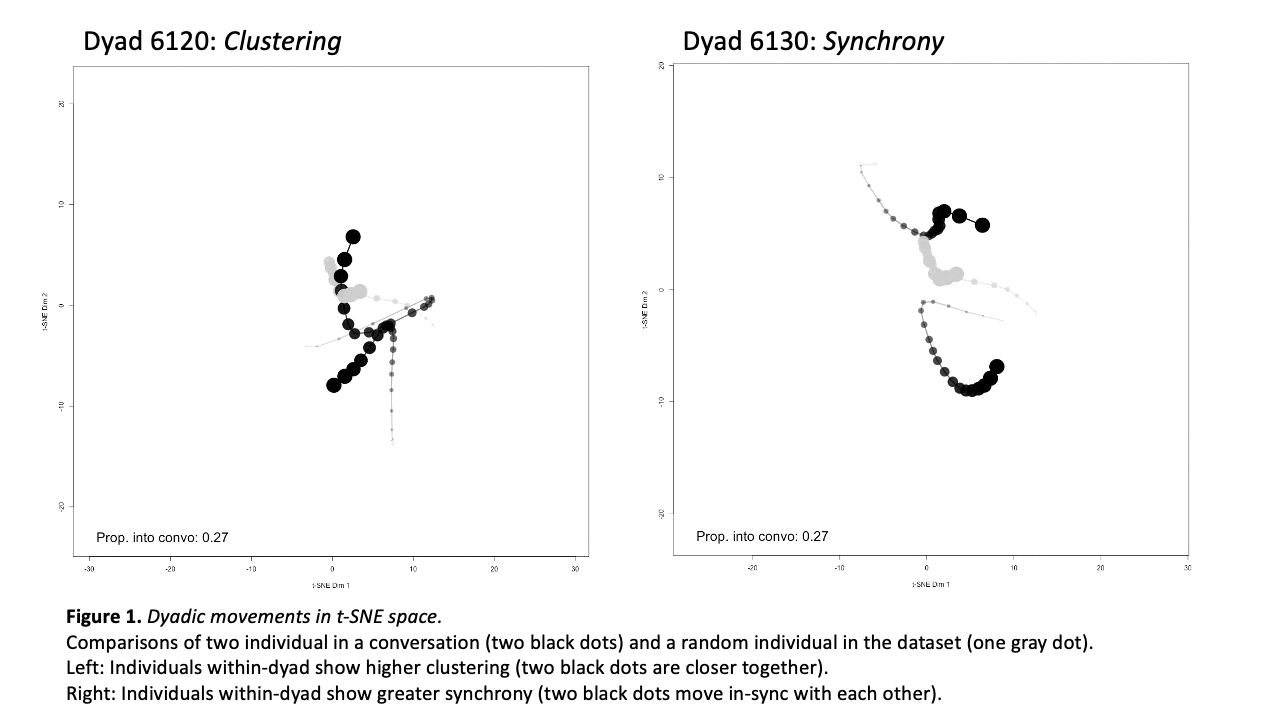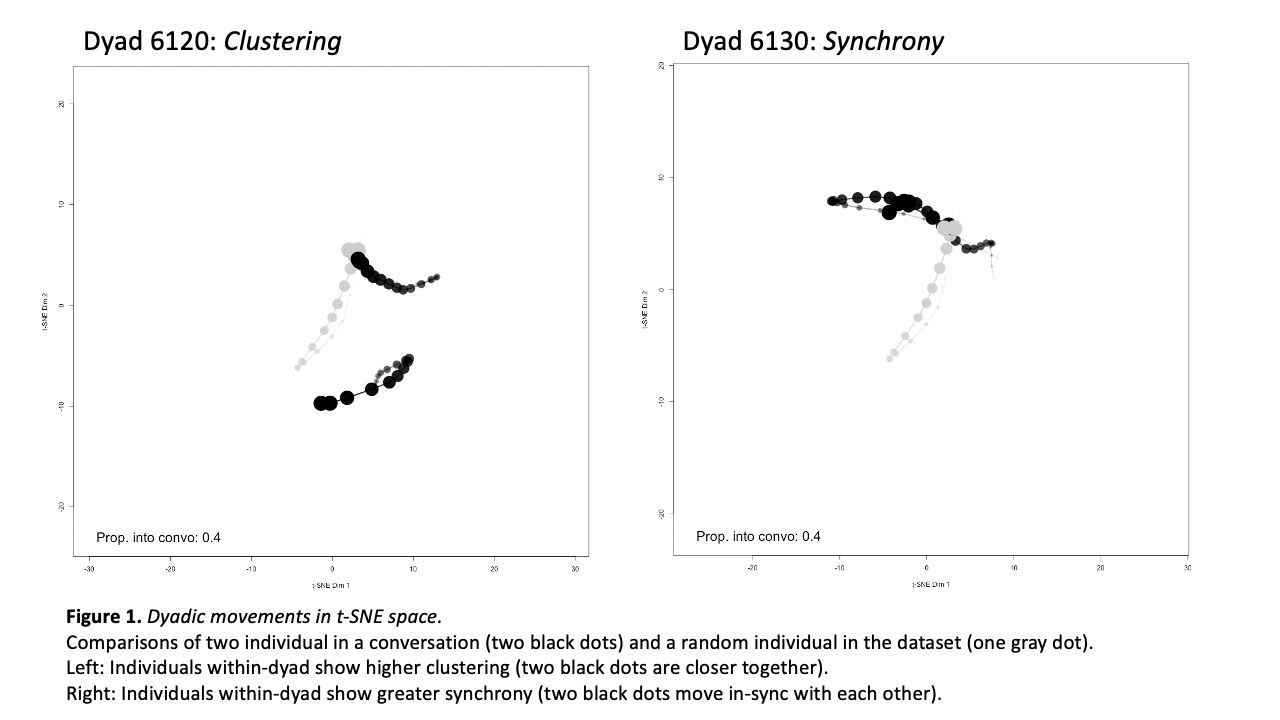
Computational Social Science
Applied Deep Learning | Machine Learning | Social Media
Applied Deep Learning, Computer Vision and Multimodal Neural Network
-
Jiang, Y., (2023). Emotions in Presidential Debates: A Deep-Learning Approach for Detecting Multimodal Affect. Exploring the C-SPAN Archives : Advancing the Research Agenda. In-prepare
-
Jiang, Y. (2023). Automated Nonverbal Cue Detection in Political-Debate Videos: An Optimized RNN-LSTM Approach. Communications in Computer and Information Science. Springer, doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-49212-9_5
Applied Machine Learning, Social Media and Social Movements
-
Jiang, Y., Jin, X. & Deng, Q. (2022). Short Video Uprising: How #BlackLivesMatter content on TikTok challenges the protest paradigm. Workshop Proceedings of the 16th ICWSM Conference on Images in Online Political Communication (PhoMemes). doi: 10.36190/2022.42
-
Shea, C. S., Jiang, Y., & Leung, W. L. (2022). David vs. Goliath: transnational grassroots outreach and empirical evidence from the # HongKongProtests Twitter network. Review of Communication, 22(3), 193-212. 10.1080/15358593.2022.2106793
-
Chen, Y., Shi, Y., Luo, J., Jiang, Y. et al. (2022). How Is Vaping Framed on Online Knowledge Dissemination Platforms?. In: Thomson, R., Dancy, C., Pyke, A. (eds) Social, Cultural, and Behavioral Modeling. SBP-BRiMS 2022, vol 13558. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-17114-7_7
Computational Tools and Validation
-
Akcakir, G., Jiang, Y., Luo, J., & Noh, S. (2023). Validating a Mixed-Method Approach for Multilingual News Framing Analysis: A case study of COVID-19. Computational Communication Research, 5(2). https://doi.org/10.5117/CCR2023.2.11.AKCA
-
Lai, S., Jiang, Y., Lei, G., Betke, M., Ishwar, P., & Wijaya, D. An Unsupervised Approach to Discover Media Frames. Proceedings of The LREC 2022 workshop on NLP for Political Sciences. par.nsf.gov/biblio/10347514
Ethnographic Fieldwork
-
Chee, W.C., & Jiang, Y. (2023). Understanding the Sociopolitical Participation of Ethnic Minority in Hong Kong: A Cultural Citizenship Study Approach. Ethnic and Racial Studies (SI proposal accepted)